Arts Menu
An Introduction to WHMIS for Visual Art Students
WHMIS — Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System
The three key elements of WHMIS:
- WHMIS labels: Labels on controlled products alert workers to the identity of the product, hazards, and precautionary measures.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Technical bulletins provide detailed hazard and precautionary information.
- WHMIS education and training programs: The employer provides education and training for workers so that they can work safely with and near controlled products.
Workers (students) need to know how WHMIS works, the hazards of controlled products in their workplace (studio), and the safe work procedures they must follow.
Pictograms are graphic images that immediately show the user of a hazardous product what type of hazard is present. With a quick glance, you can see, for example, that the product is flammable or that it might be a health hazard.
Most pictograms have a distinctive red "square set on one of its points" border. Inside this border is a symbol that represents the potential hazard (e.g., fire, health hazard, corrosive, etc.). Together, the symbol and the border are referred to as a pictogram. Pictograms are assigned to specific hazard classes or categories.
The graphic below shows hazard pictograms. The bold type is the name given to the pictogram; the words in the brackets describe the hazard.

|
Exploding bomb (for explosion or reactivity hazards) |

|
Flame (for fire hazards) |

|
Flame over circle (for oxidizing hazards) |

|
Gas cylinder (for gases under pressure) |
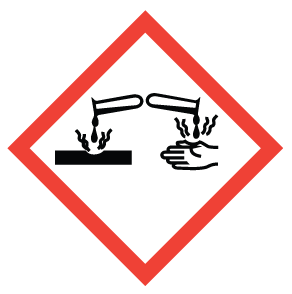
|
Corrosion (for corrosive damage to metals, as well as skin, eyes) |

|
Skull and Crossbones (can cause death or toxicity with short exposure to small amounts) |

|
Health hazard (may cause or suspected of causing serious health effects) |

|
Exclamation mark (may cause less serious health effects or damage the ozone layer*) |

|
Environment (may cause damage to the aquatic environment) |

|
Biohazardous Infectious Materials (for organisms or toxins that can cause diseases in people or animals) |
Note
* The GHS system also defines an Environmental hazards group. This group (and its classes) was not adopted in WHMIS 2015. However, you may see the environmental classes listed on labels and Safety Data Sheets (SDSs). Including information about environmental hazards is allowed by WHMIS 2015.
WHMIS Labels
The purpose of labels is to alert workers to the main hazards of controlled products and provide instructions for safe handling, and to direct workers to the SDS for more information. The two types of WHMIS labels are the supplier label and the workplace label. Other means of identification may be used where appropriate (such as warning signs, colour codes, placards).
SUPPLIER LABEL contains the following:
- Product identifier - the brand name, chemical name, common name, generic name, or trade name of the hazardous product
- Initial supplier identifier - the name, address, and telephone number of manufacturer or importer
- Pictogram(s) - hazard symbol usually contained within a red diamond-shaped boarder
- Signal word - a word used to alert the reader to potential hazards and to indicate the severity of the hazard
- Hazard statement(s) - standardized phrases that describe the nature of the hazard posed by the hazardous product
- Precautionary statement(s) - standardizes phrases that describe measure to be taken to minimize or prevent adverse effects resulting from espouse or improper handling or storage of the hazardous product
WORKPLACE LABEL contains the following:
- Product name
- Safe handling information
- Reference to the SDS
Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) are documents that provide information about the hazards of a product and advice about safety precautions.
WHMIS 2015 requires a standard 16 section SDS with all information in a specific order. SDSs are complex and technical and you will not be asked to memorize the sections but you must understand that an SDS provides detailed information on a hazardous product and should be reviewed before working with the product.
- Identification
- Hazard identification
- Compositions/information on ingredients
- First aid measures
- Fire fighting measures
- Accidental release measures
- Handling and storage
- Exposure controls/personal protection
- Physical and chemical properties
- Stability and reactivity
- Toxicological information
- Ecological information
- Disposal considerations
- Transport information
- Regulatory information
- Other information
WHMIS Implementation — Education and Training
An employer must ensure workers receive general WHMIS education on:
- Hazards of controlled products in use at the workplace
- Rights and responsibilities
- Content required on labels and MSDS, and the significance of this information
- Elements of the WHMIS program
An employer must ensure instruction in specific procedures safe use, storage, handling and disposal of a controlled product in transit:
- in case of an escape of a controlled product
- in an emergency involving a controlled product
Workers who are successfully educated and trained in WHMIS should be able to answer these four questions:
- What are the hazards of the product?
- How do I protect myself? What should I do in case of an emergency?
- Where do I obtain more information?
For more information and training, please visit:
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System

