Science Menu
What is Data Science?
Data science combines multiple fields—including statistics, scientific methods, artificial intelligence, and data analysis—to extract value from data. Data science professionals combine a range of skills to analyze data collected from the web, smartphones, customers, sensors, and other sources to determine actionable insights.
Data science encompasses preparing data for analysis, including cleansing, aggregating, and manipulating the data to perform advanced data analysis. Analytic applications and data scientists can then review the results to uncover patterns and enable business leaders to draw informed insights.
Data science reveals trends and produces insights that businesses can use to make better decisions and create more innovative products and services. Perhaps most importantly, it enables machine learning models to learn from the vast amounts of data being fed to them, rather than mainly relying upon business analysts to see what they can discover from the data.
What Does a Data Science Professional Do?
Data science professionals need to be curious and result-oriented and pay attention to details. They also require exceptional industry-specific knowledge and communication skills that allow them to explain highly technical results to their non-technical counterparts. They possess a strong quantitative background in statistics and linear algebra as well as programming knowledge with focuses in data warehousing, mining, and modeling to build and analyze algorithms.
Key technical tools and skills include:
- R
- Python
- Apache Hadoop
- MapReduce
- Apache Spark
- NoSQL databases
- Cloud computing
- Apache Pig
- Tableau
- iPython notebooks
- GitHub
The Data Science Life Cycle
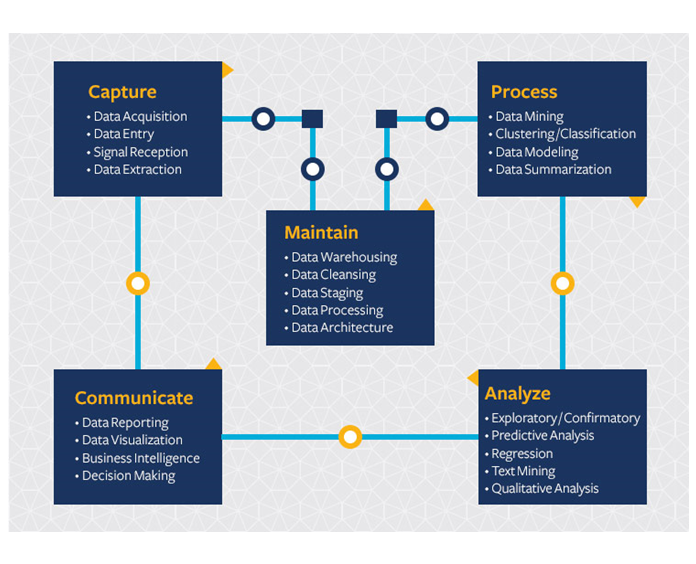
The five stages of the data science life cycle
The five stages consists of Capture, Maintain, Process, Analyze and Communicate.
- Capture (data acquisition, data entry, signal reception, data extraction);
- Maintain (data warehousing, data cleansing, data staging, data processing, data architecture);
- Process (data mining, clustering/classification, data modeling, data summarization);
- Analyze (exploratory/confirmatory, predictive analysis, regression, text mining, qualitative analysis);
- Communicate (data reporting, data visualization, business intelligence, decision making).

